
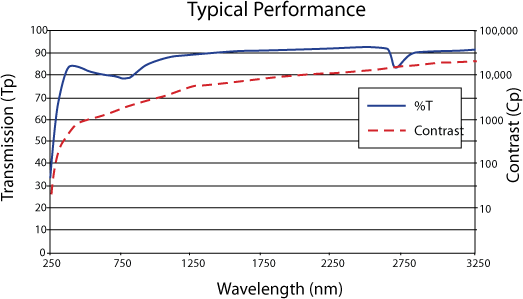
Ultra Broadband Wire Grid Polarizers consist of a thin layer of aluminum MicroWires layered between two Fused Silica windows. Designed for multi-wavelength applications, these polarizers have excellent heat resistance and performance beginning in the UV and extending into the infrared (IR). The polarizers feature a fused silica substrate. Ultra Broadband Wire Grid Polarizers reflect S-polarized light and transmit P-polarized light. These polarizers are available in a variety of thicknesses and clear apertures, in either a 12.5, 25, or 50mm diameter.
Note: The input beam should be oriented towards the cover glass side, indicated by a reference mark which also indicates the direction of the transmission axis.
Wire Grid Polarizers are constructed by attaching MicroWires to the first window, and then applying a thin cover glass onto the wire grid surface to protect the wire from damage. The light is polarized by the birefringent nature of the wire grid surface. When incident light strikes the wire grid, P-polarized light contacts a dielectric and is transmitted, while S-polarized light contacts a mirror and is reflected.
or view regional numbers
QUOTE TOOL
enter stock numbers to begin
Copyright 2024, Edmund Optics Singapore Pte. Ltd, 18 Woodlands Loop #04-00, Singapore 738100
California Consumer Privacy Acts (CCPA): Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
California Transparency in Supply Chains Act